Page 34 - AUN-QA
P. 34
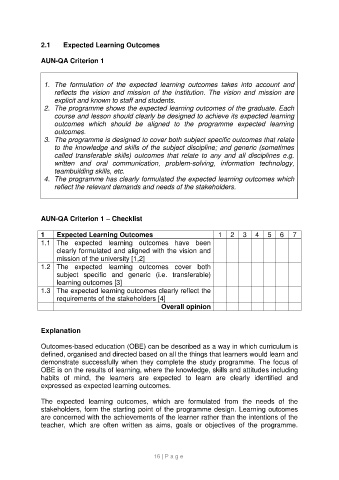
2.1 Expected Learning Outcomes
AUN-QA Criterion 1
1. The formulation of the expected learning outcomes takes into account and
reflects the vision and mission of the institution. The vision and mission are
explicit and known to staff and students.
2. The programme shows the expected learning outcomes of the graduate. Each
course and lesson should clearly be designed to achieve its expected learning
outcomes which should be aligned to the programme expected learning
outcomes.
3. The programme is designed to cover both subject specific outcomes that relate
to the knowledge and skills of the subject discipline; and generic (sometimes
called transferable skills) outcomes that relate to any and all disciplines e.g.
written and oral communication, problem-solving, information technology,
teambuilding skills, etc.
4. The programme has clearly formulated the expected learning outcomes which
reflect the relevant demands and needs of the stakeholders.
AUN-QA Criterion 1 – Checklist
1 Expected Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1.1 The expected learning outcomes have been
clearly formulated and aligned with the vision and
mission of the university [1,2]
1.2 The expected learning outcomes cover both
subject specific and generic (i.e. transferable)
learning outcomes [3]
1.3 The expected learning outcomes clearly reflect the
requirements of the stakeholders [4]
Overall opinion
Explanation
Outcomes-based education (OBE) can be described as a way in which curriculum is
defined, organised and directed based on all the things that learners would learn and
demonstrate successfully when they complete the study programme. The focus of
OBE is on the results of learning, where the knowledge, skills and attitudes including
habits of mind, the learners are expected to learn are clearly identified and
expressed as expected learning outcomes.
The expected learning outcomes, which are formulated from the needs of the
stakeholders, form the starting point of the programme design. Learning outcomes
are concerned with the achievements of the learner rather than the intentions of the
teacher, which are often written as aims, goals or objectives of the programme.
16 | P a g e